Applications of First Law of Thermodynamics
Applications of First Law of Thermodynamics: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Enthalpy, Work Done in Reversible Isothermal Expansion, Work Done in Reversible Adiabatic Process, Graph of Adiabatic Process, Graph of Isobaric Process and, Work Done in Irreversible Adiabatic Process
Important Questions on Applications of First Law of Thermodynamics
moles of an ideal gas expands isothermally against a constant pressure of Pascal from L.The amount of work involved is
The enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of
and for the following process for a monoatomic gas are:
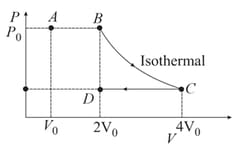
Consider the reversible isothermal expansion of an ideal gas in a closed system at two different temperatures and The correct graphical depiction of the dependence of work done on the final volume
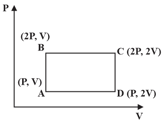
A thermodynamic cycle in the pressure -volume plane is given below:
and are isothermal processes while and are adiabatic processes. The same cycle in the temperature - entropy plane is :
During the free expansion of an ideal gas in an isolated chamber,
A piston filled with of an ideal gas expands reversibly from to at a constant temperature of . As it does so, it absorbs of heat. The values of and for the process will be
() ()
One mole of an ideal gas (at ) is expanded from volume to at constant temperature. The value of work done (in ), if gas is expanded against vacuum ?
For next two question please follow the same
Work done by the system in isothermal reversible process is: . Also in case of adiabatic reversible process work done by the system is given by: . During expansion disorder increases and the increase in disorder is expressed in terms of change in entropy . Both entropy and enthalpy changes obtained for a process were taken as a measure of spontaneity of process but finally it was recommended that decrease in free energy is responsible for spontaneity and .
Which of the following statements are correct:
(1) The expansion work for a gas into vacuum is equal to zero.(2) 1 mole of a gas occupying 3 litre volume on expanding to 15 litre at constant pressure of 1 atm does expansion work 1.215 kJ.
(3) The maximum work done during expansion of 16 g at 300 K from to is
(4) The for is almost negligible in comparison to for .
(5) (At constant T)
For next two question please follow the same
A sample of an ideal gas is expanded to twice its original volume of 1 m3 in a reversible process for which and at constant volume.
The work done during the process may be
moles of an ideal gas with at held in cylinder fitted with piston is expanded reversibly and isothermally to three times volume (initially ). The cylinder placed in an insulated container and pressure returned to adiabatically in one step when mechanical equilibrium is reached. Read the passage and answer the questions as single choice correct.
The volume at point may be
For next two question please follow the same
moles of an ideal gas with at , held in cylinder fitted with piston is expanded reversibly and isothermally to three times volume (initially ). The cylinder placed in an insulated container and pressure returned to adiabatically in one step when mechanical equilibrium is reached. Read the passage and answer the questions as single choice correct.
process may be
One mol of a non-ideal gas undergoes a change of state with a change in internal energy, . The change in enthalpy of the process in is
Among the following, which expression is most accurate to calculate the work done by gas in reversible isothermal expansion?
On the basis of following data , calculate the heat of reaction for the given process.
If of is added to of solution of same strength, increment in temperature takes place. If of same solution is mixed with of same solution, temperature increases by-
Which of the following relationship between x and y will be true when equal volumes of and are neutralized completely by dil. NaOH solution and and heat are liberated respectively?
The value of is The enthalpy of formation of of water in gaseous state from and is:
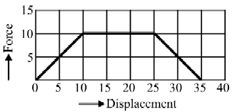
Adjacent figure shows the force-displacement graph of a moving body, the work done in displacing body from to by the shown force is equals to
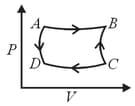
An ideal monoatomic gas is taken round the cycle. ABCDA as shown in figure. The work done during the cycle is